Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Futemma, Akira; Sanada, Yukihisa; Sasaki, Miyuki; Kawasaki, Yoshiharu*; Iwai, Takeyuki*; Hiraga, Shogo*; Haginoya, Masashi*; Matsunaga, Yuki*; Akutsu, Yuichiro*; Arai, Yoshinori*; et al.
JAEA-Technology 2023-026, 161 Pages, 2024/03
By the accident at Tokyo Electric Power Company's (TEPCO's) Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (FDNPS), caused by tsunami triggered by the 2011 off the Pacific coast of Tohoku Earthquake, a large amount of radioactive material was released into the surrounding environment. After the accident, Airborne Radiation Monitoring (ARM) via manned helicopter has been utilized as a method to quickly and extensively measure radiation distribution surrounding FDNPS. In order to utilize ARM and to promptly provide the results during a nuclear emergency, information on background radiation levels, topographical features, and controlled airspace surrounding nationwide nuclear facilities have been prepared in advance. In the fiscal year 2022, we conducted ARM around the Mihama Nuclear Power Station of Kansai Electric Power Company (KEPCO), the Tsuruga Power Station of Japan Atomic Power Company (JAPC), and the Ikata Power Station of Shikoku Electric Power Company (YONDEN), and prepared information on background radiation doses and controlled airspace. In addition, we have developed an aerial radiation detection system via unmanned airplane, which is expected to be an alternative to ARM, during a nuclear emergency. This report summarizes the results and technical issues identified.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Ochi, Kotaro; Ishizaki, Azusa
JAEA-Research 2020-006, 60 Pages, 2020/07
At the accident of nuclear facilities, a prediction of the behavior of released radioactive plume is indispensable to make a decision on a refuge plan of inhabitants. Currently, prediction system which is based on atmospheric dispersion simulation has been implemented as a tool of the atomic energy disaster prevention. However, the direct measurement method of the radioactive plume has not existed. In this study, some component technologies were developed for the establishment of direct measurement methods of radioactive plume using unmanned aerial vehicle whose technological innovation is remarkable. In addition, the spray test using mock aerosol was conducted to obtaining the deposition rate to the airplane body. The algorism of making a flight plan was developed based on a prediction model of the radioactive plume. This report summarized the outcome of the last year of the three-year plan.
Matsuura, Yuto*; Hayano, Akira; Itakura, Kenichi*; Suzuki, Yukinori*
Applied Soft Computing, 84, p.105737_1 - 105737_9, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:14.62(Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence)LiDAR (laser imaging detection and ranging) has been developed to obtain a high-resolution point cloud data indicating the detailed 3D shapes of an object. To identify discontinuities in a rock mass of a tunnel gallery wall, it is necessary to approximate the rock mass surface with small planes. Normal vectors of the planes are important to identify discontinuities. We developed an algorithm for estimation of planes based on multi-dimensional particle swarm optimization (MD PSO) from point cloud data. Point cloud data were segmented into bounding boxes and grouped into clusters by MD PSO. Planes were estimated using the least squares method for point cloud data in the respective clusters. The newly developed MD PSO algorithm was evaluated using point cloud data obtained from a gallery wall. Evaluation was carried out in comparison with the previous developed variable-box segmentation (VBS) algorithm. The MD PSO-based algorithm showed a 7% higher accuracy than that of the VBS algorithm.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Arima, Hiroshi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*
High Pressure Research, 39(3), p.417 - 425, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:81.85(Physics, Multidisciplinary)We have developed a technique for neutron diffraction experiments at pressures up to 40 GPa using a Paris-Edinburgh press at the PLANET beamline in J-PARC. To increase the maximum accessible pressure, the diameter of the dimple for sample chamber at the top of the sintered diamond anvils is sequentially reduced from 4.0 mm to 1.0 mm. As a result, the maximum pressure increased and finally reached 40 GPa. By combining this technique with the beam optics which defines the gauge volume, diffraction patterns sufficient for full-structure refinements are obtainable at such pressures.
Sanada, Yukihisa; Nishizawa, Yukiyasu*; Ochi, Kotaro; Yuki, Yoichi*; Ishizaki, Azusa; Osada, Naoyuki*
JAEA-Research 2018-009, 48 Pages, 2019/01
At the accident of nuclear facilities, a prediction of the behavior of released radioactive plume is indispensable to make a decision on a refuge plan of inhabitants. Currently, prediction system which is based on atmospheric dispersion simulation has been implemented as a tool of the atomic energy disaster prevention. However, the direct measurement method of the radioactive plume has not existed. In this study, some component technologies were developed for the establishment of direct measurement methods of radioactive plume using unmanned aerial vehicle whose technological innovation is remarkable. In addition, the spray test using mock aerosol was conducted to obtaining the deposition rate to the airplane body. The algorism of making a flight plan was developed based on a prediction model of the radioactive plume. This report summarized the outcome of the second year of the three-year plan.
 H
H - C
- C F
F cocrystal towards graphane structure
cocrystal towards graphane structureWang, Y.*; Dong, X.*; Tang, X.*; Zheng, H.*; Li, K.*; Lin, X.*; Fang, L.*; Sun, G.*; Chen, X.*; Xie, L.*; et al.
Angewandte Chemie; International Edition, 58(5), p.1468 - 1473, 2019/01
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:80.32(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Pressure-induced polymerization (PIP) of aromatics is a novel method to construct sp -carbon frameworks, and nanothreads with diamond-like structures were synthesized by compressing benzene and its derivatives. Here by compressing benzene-hexafluorobenzene cocrystal(CHCF), we identified H-F-substituted graphane with a layered structure in the PIP product. Based on the crystal structure determined from the in situ neutron diffraction and the intermediate products identified by the gas chromatography-mass spectrum, we found that at 20 GPa CHCF forms tilted columns with benzene and hexafluorobenzene stacked alternatively, which leads to a [4+2] polymer, and then transfers to short-range ordered hydrogenated-fluorinated graphane. The reaction process contains [4+2] Diels-Alder, retro-Diels-Alder, and 1-1' coupling, and the former is the key reaction in the PIP. Our studies confirmed the elemental reactions of the CHCF for the first time, which provides a novel insight into the PIP of aromatics.
-carbon frameworks, and nanothreads with diamond-like structures were synthesized by compressing benzene and its derivatives. Here by compressing benzene-hexafluorobenzene cocrystal(CHCF), we identified H-F-substituted graphane with a layered structure in the PIP product. Based on the crystal structure determined from the in situ neutron diffraction and the intermediate products identified by the gas chromatography-mass spectrum, we found that at 20 GPa CHCF forms tilted columns with benzene and hexafluorobenzene stacked alternatively, which leads to a [4+2] polymer, and then transfers to short-range ordered hydrogenated-fluorinated graphane. The reaction process contains [4+2] Diels-Alder, retro-Diels-Alder, and 1-1' coupling, and the former is the key reaction in the PIP. Our studies confirmed the elemental reactions of the CHCF for the first time, which provides a novel insight into the PIP of aromatics.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Abe, Jun*; Funakoshi, Kenichi*; Okazaki, Nobuo*
Nihon Kessho Gakkai-Shi, 59(6), p.301 - 308, 2017/12
PLANET is a neutron beamline dedicated to high-pressure experiments. Combining the intense neutron source of J-PARC and high-pressure devices designed for time-of-flight powder neutron diffraction enables precise structure analysis of crystal, liquid and amorphous solids over wide pressure and temperature region of 0-20 GPa and 77-2000K. This beamline is effective for various studies in geophysics, planetary science, physics and chemistry. This paper overviews the beamline and introduces recent results obtained at PLANET.
Klotz, S.*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Kunc, K.*; Sano, Asami; Machida, Shinichi*; Hattori, Takanori
Physical Review B, 95(17), p.174111_1 - 174111_7, 2017/05
Times Cited Count:35 Percentile:81.94(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The compression behaviour of deuterated ice VII and VIII was investigated by high pressure neutron scattering in the pressure range 2-13.7 GPa between 93 K and 300 K. We establish equations-of-state which contain accurate values for the bulk moduli B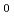 , their pressure derivatives B'
, their pressure derivatives B'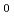 , as well as the ambient pressure volumina V
, as well as the ambient pressure volumina V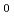 . These equations-of-state hold over a large part of the stability domain of ice VII, by comparison with available X-ray data, and to at least
. These equations-of-state hold over a large part of the stability domain of ice VII, by comparison with available X-ray data, and to at least  13 GPa for ice VIII. They are indistinguishable at low pressures, but beyond
13 GPa for ice VIII. They are indistinguishable at low pressures, but beyond  7 GPa and at low temperatures ice VIII appears to become stiffer than expected. This might be related to an anomalous phonon hardening observed previously in ice VIII in this
7 GPa and at low temperatures ice VIII appears to become stiffer than expected. This might be related to an anomalous phonon hardening observed previously in ice VIII in this 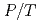 range [D.D. Klug et al., Physical Review B, 70, 144113 (2004)].
range [D.D. Klug et al., Physical Review B, 70, 144113 (2004)].
Sato, Masayuki*; Muraoka, Koji*; Hozumi, Koki*; Sanada, Yukihisa; Yamada, Tsutomu*; Torii, Tatsuo
Nihon Koku Uchu Gakkai Rombunshu (Internet), 65(2), p.54 - 63, 2017/02
This paper is concerned with the design problem of preview altitude controller for Unmanned Airplane for Radiation Monitoring System (UARMS) to improve its control performance. UARMS has been developed for radiation monitoring around Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant which spread radiation contaminant due to the huge tsunamis caused by the Great East Japan Earthquake. The monitoring area contains flat as well as mountain areas. The basic flight controller has been confirmed to have satisfactory performance with respect to altitude holding; however, the control performance for variable altitude commands is not sufficient for practical use in mountain areas. We therefore design preview altitude controller with only proportional gains by considering the practicality and the strong requirement of safety for UARMS. Control performance of the designed preview controller was evaluated by flight tests conducted around Fukushima Sky Park.
Kato, Chiaki; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamamoto, Masahiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 53(9), p.1371 - 1379, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:36.27(Nuclear Science & Technology)The effects of crystal textures and the potentials in the anodic oxidation of zirconium in a boiling nitric acid solution were investigated to study the stress corrosion cracking of zirconium in nitric acid solutions. The growth of the zirconium oxide film dramatically changed depending on the applied potential at a closed depassivation potential (1.47 V vs. SSE). At 1.5 V, the zirconium oxide film rapidly grows, and its growth exhibits cyclic oxidation kinetics in accordance with a nearly cubic rate law. The zirconium oxide film grows according to the quantity of electric charge, and the growth rate does not depend on the crystal texture in the pretransition region before the cyclic oxidation kinetics. However, the growth and cracking under the thick oxide film depend on the crystal texture in the transition region. On the normal direction side, the oxide film thickness decreases on average since some areas of the thick oxide film are separated from the specimen surface owing to the cracks in the thick oxide. On the rolling direction side, cracks are found under the thick oxide film, which deeply propagate along the RD without an external stress. The cracks under the thick oxide film propagate to the center of the oxide layer. The cracks in the oxide layer propagate in the (0002)Zr plane in the zirconium matrix. The oxide layer consists of string-like zirconium oxide and zirconium hydride. The string-like zirconium oxide contains orthorhombic ZrO in addition to monoclinic ZrO
in addition to monoclinic ZrO . As one assumption for the mechanism of crack initiation and propagation without an external stress, it is considered that the oxidizing zirconium hydrides precipitate in the (0002)Zr and then the phase transformation from orthorhombic ZrO
. As one assumption for the mechanism of crack initiation and propagation without an external stress, it is considered that the oxidizing zirconium hydrides precipitate in the (0002)Zr and then the phase transformation from orthorhombic ZrO to monoclinic ZrO
to monoclinic ZrO in the oxide layer causes the crack propagation in the (0002) plane.
in the oxide layer causes the crack propagation in the (0002) plane.
Hattori, Takanori; Sano, Asami; Arima, Hiroshi*
Hamon, 26(2), p.85 - 90, 2016/05
PLANET is the first neutron powder diffractometer dedicated to high-pressure and high-temperature experiments in the World. The six-axis press designed for this beamline enables routine data collection at pressures and temperatures up to 10 GPa and 2000K. In this article, we introduce how the PLANET had been constructed.
Hattori, Takanori
Hamon, 25(3), p.231 - 237, 2015/08
PLANET is a time-of-flight (TOF) neutron beamline dedicated to high-pressure experiments. By using several high-pressure devices, neutron diffraction patterns are obtainable at wide PT condition, ranging from 0-20 GPa and 77 K-2000 K. To obtain clean pattern, the beamline is equipped with the incident slits and receiving collimators to eliminate parasitic scattering from the high-pressure cell. The high performance of the diffractometer with the resolution ( d/d = 0.6%) and the accessible d-spacing range (0.2-8.4
d/d = 0.6%) and the accessible d-spacing range (0.2-8.4  ) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids even under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions.
) together with low-parasitic scattering characteristics enables precise structure determination of crystals and liquids even under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions.
Komatsu, Kazuki*; Shinozaki, Ayako*; Machida, Shinichi*; Matsubayashi, Takuto*; Watanabe, Mao*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori
Acta Crystallographica Section B; Structural Science, Crystal Engineering and Materials (Internet), 71(1), p.74 - 80, 2015/02
Times Cited Count:19 Percentile:79.49(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Magnesium dichloride decahydrate (MgCl 10H
10H O) and its deuterated counterpart (MgCl
O) and its deuterated counterpart (MgCl 10D
10D O) are identified for the first time by in-situ powder synchrotron X-ray and spallation neutron diffraction. These substances are crystallized from a previously unidentified nanocrystalline compound, which originates from an amorphous state at low temperature. A combination of a recently developed autoindexing procedure and the charge-flipping method reveals that the crystal structure of MgCl 10H
O) are identified for the first time by in-situ powder synchrotron X-ray and spallation neutron diffraction. These substances are crystallized from a previously unidentified nanocrystalline compound, which originates from an amorphous state at low temperature. A combination of a recently developed autoindexing procedure and the charge-flipping method reveals that the crystal structure of MgCl 10H O consists of an ABCABC... sequence of Mg(H
O consists of an ABCABC... sequence of Mg(H O)
O) octahedra. The Cl
octahedra. The Cl anions and remaining water molecules unconnected to the Mg
anions and remaining water molecules unconnected to the Mg cations bind the octahedra, similar to other water-rich magnesium dichloride hydrates. The D positions in MgCl
cations bind the octahedra, similar to other water-rich magnesium dichloride hydrates. The D positions in MgCl 10D
10D O, determined by the difference Fourier methods using the neutron powder diffraction patterns at 2.5 GPa, show the features such as bifurcated hydrogen bonds and tetrahedrally coordinated O atoms.
O, determined by the difference Fourier methods using the neutron powder diffraction patterns at 2.5 GPa, show the features such as bifurcated hydrogen bonds and tetrahedrally coordinated O atoms.
Hattori, Takanori; Akutsu, Kazuhiro*; Suzuki, Junichi*
Bunseki, 2015(2), p.58 - 64, 2015/02
In the J-PARC MLF, 18 beamlines has been constructed and many studies on scientific and industrial use have been performed. This paper introduces the high-pressure science at high-pressure neutron diffractometer "PLANET" and surface/interface structure analysis at vertical sample geometry polarized neutron reflectometer "SHARAKU".
Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Arima, Hiroshi*; Yamada, Akihiro*; Tabata, Satoshi*; Kondo, Masahiro*; Nakamura, Akihiro*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Yagi, Takehiko*
Review of Scientific Instruments, 85(11), p.113905_1 - 113905_8, 2014/11
Times Cited Count:43 Percentile:84.12(Instruments & Instrumentation)We developed a six-axis multi-anvil press, ATSUHIME, for high-pressure and high-temperature in situ time-of-flight neutron powder diffraction experiments. The press has six orthogonally oriented hydraulic rams that operate individually to compress a cubic sample assembly. Experiments indicate that the press can generate pressures up to 9.3 GPa and temperatures up to 2000 K using a 6-6-type cell assembly, with available sample volume of about 50 mm  . Using a 6-8-type cell assembly, the available conditions expand to 16 GPa and 1273 K. Combination of the six-axis press and the collimation devices realized high-quality diffraction pattern with no contamination from the heater or the sample container surrounding the sample. This press constitutes a new tool for using neutron diffraction to study the structures of crystals and liquids under high pressures and temperatures.
. Using a 6-8-type cell assembly, the available conditions expand to 16 GPa and 1273 K. Combination of the six-axis press and the collimation devices realized high-quality diffraction pattern with no contamination from the heater or the sample container surrounding the sample. This press constitutes a new tool for using neutron diffraction to study the structures of crystals and liquids under high pressures and temperatures.
Iizuka, Riko*; Komatsu, Kazuki*; Kagi, Hiroyuki*; Nagai, Takaya*; Sano, Asami; Hattori, Takanori; Goto, Hirotada*; Yagi, Takehiko*
Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 218, p.95 - 102, 2014/10
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:33.69(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)In situ neutron diffraction measurements combined with the pulsed neutron source at the Japan Proton Accelerator Research Complex (J-PARC) were conducted on high-pressure polymorphs of deuterated portlandite (Ca(OD) ) using a Paris-Edinburgh cell and a multi-anvil press. The atomic positions including hydrogen for the unquenchable high-pressure phase at room temperature (phase II') were first clarified. The bent hydrogen bonds under high pressure were consistent with results from Raman spectroscopy. The structure of the high-pressure and high-temperature phase (Phase II) was concordant with that observed previously by another group for a recovered sample. The observations elucidate the phase transition mechanism among the polymorphs, which involves the sliding of CaO polyhedral layers, position modulations of Ca atoms, and recombination of Ca-O bonds accompanied by the reorientation of hydrogen to form more stable hydrogen bonds.
) using a Paris-Edinburgh cell and a multi-anvil press. The atomic positions including hydrogen for the unquenchable high-pressure phase at room temperature (phase II') were first clarified. The bent hydrogen bonds under high pressure were consistent with results from Raman spectroscopy. The structure of the high-pressure and high-temperature phase (Phase II) was concordant with that observed previously by another group for a recovered sample. The observations elucidate the phase transition mechanism among the polymorphs, which involves the sliding of CaO polyhedral layers, position modulations of Ca atoms, and recombination of Ca-O bonds accompanied by the reorientation of hydrogen to form more stable hydrogen bonds.
Hattori, Hirofumi*; Sato, Hiroshi; Nagano, Yasutaka*
Nihon Kikai Gakkai Rombunshu, B, 70(696), p.1919 - 1926, 2004/08
no abstracts in English
Kinouchi, Nobuyuki; Oishi, Tetsuya; Yoshida, Makoto
Radioisotopes, 50(5), p.183 - 189, 2001/05
no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hideo; Ito, Kazuhiro*; Kukita, Yutaka*; *; ; Maekawa, Hiroshi; Katsuta, Hiroji
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 258-263, p.440 - 445, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:53.73(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
Nakamura, Hideo; *; Kukita, Yutaka*; *; ; Maekawa, Hiroshi
Eighth Int. Topical Meeting on Nuclear Reactor Thermal-Hydraulics (NURETH-8), 3, p.1268 - 1275, 1997/00
no abstracts in English